If you need to schedule a background task on Android, you’re probably familiar with all of the various ways to accomplish this such as:
- Google Cloud Messaging
- Firebase Cloud Messaging
- DownloadManager
- Foreground Service
- Alarm Manager
- etc
WorkManager
Give a warm welcome to WorkManager. WorkManager is a library that makes it easy to schedule deferrable, asynchronous tasks even if the app exits or the device restarts. It was designed to be backwards compatible to API 14 and does so by wrapping JobScheduler, AlarmManager, and BroadcastReceivers all in one.
Using JobScheduler your app will be running on a device that is API 23+. Anything below, you’ll be using a combination of AlarmManager + BroadcastReceivers.
How is work executed?
Work is fed to an executor to guarantee the work is done.

The executor will complete the work so long as it meets the constraints that you set up when you enqueue the work.
Async by Default
Every operation is asynchronous. Thus you won’t have to worry about threading at all. The operations are saved in a WorkManager database that is the source of truth for any enqueued, successful, or cancelled operations.
When does work end?
- Upon the work finishing.
- In the event that the constraints are no longer met (Network could be lost, Phone is no longer plugged in, etc).
- The OS decided to kill your enqueued work.
- You cancelled your work.
Lifetime of work
One Time Work
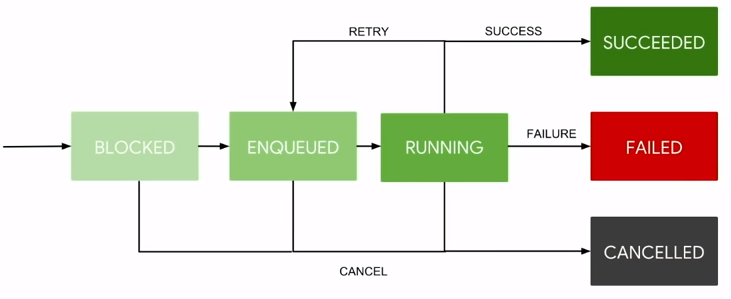
This type of work’s final state is Succeeded when completed. Otherwise it will go into a Failed or Cancelled state.
Periodic Work

This type of work does not have a final state because it has either a finite or infinite amount of iterations. Thus it will continuously enqueue and run.
Getting Started
Installing the NuGet
Using NuGet, install the Xamarin.Android.Arch.Work.Runtime package into your Android application. Make sure your application is targeting Android Pie (API 28) or greater.
https://www.nuget.org/packages/Xamarin.Android.Arch.Work.Runtime/
Creating a background task
A task is defined using the Worker class. The DoWork() method is ran on a background thread provided by WorkManager.
To create a background task, extend the Worker class and override the DoWork() method. For example, to create a Worker that calculates two numbers, you can do the following:
public class CalculatorWorker : Worker
{
public CalculatorWorker(Context context, WorkerParameters workerParameters) : base(context, workerParameters)
{
}
public override Result DoWork()
{
var taxReturn = CalculateTaxes();
Android.Util.Log.Debug("CalculatorWorker", $"Your Tax Return is: {taxReturn}");
return Result.InvokeSuccess();
}
public double CalculateTaxes()
{
return 2000;
}
}
The Result returned from the DoWork() method informs you whether the task:
- Finished successfully via
Result.Success() - Failed gracefully via
Result.Failure() - Needs another attempt via
Result.Retry()
Note: Your worker only knows about the state passed into it by WorkerParameters.
When and how a task should run?
While a Worker defines the work to be done, a WorkRequest defines when and how the work should run. These tasks may be one time or periodic. You can use OneTimeWorkRequest for one time requests, and you can use PeriodicTimeWorkRequest for period time requests.
Here’s how you would build the WorkRequest for our Worker:
PeriodicWorkRequest taxWorkRequest = PeriodicWorkRequest.Builder.From<CalculatorWorker>(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(20)).Build();
Running the task
Once you’ve built the Worker and the WorkRequest, you are ready to enqueue it using WorkManager and the Enqueue() method.
WorkManager.Instance.Enqueue(taxWorkRequest);
Seeing the task
We can then use adb logcat to view our task.
2019-03-27 13:11:51.240 6364-6402/com.companyname D/CalculatorWorker: Your Tax Return is: 2000
2019-03-27 13:11:51.242 6364-6390/com.companyname I/WM-WorkerWrapper: Worker result SUCCESS for Work [ id=3735e0f9-fc12-41aa-9f51-ac856b6eac18, tags={ md5592692d8f1b606f6fbb81503ff802e0e.CalculatorWorker } ]
2019-03-27 13:21:33.020 6364-6404/com.companyname D/CalculatorWorker: Your Tax Return is: 2000
2019-03-27 13:21:33.023 6364-6390/com.companyname I/WM-WorkerWrapper: Worker result SUCCESS for Work [ id=54daa9ec-d81f-4de1-b138-d5ff6349b088, tags={ md5592692d8f1b606f6fbb81503ff802e0e.CalculatorWorker } ]
Summary
Use WorkManager for your background task needs in Android. The API is straight-forward and friendly to developers. Don’t worry about managing the lifecycle of the device and let WorkManager do the work for you.
GitHub Sample: https://github.com/JonDouglas/WorkManagerSample
The post Getting Started With WorkManager appeared first on Xamarin Blog.